Is hemp the same as cannabis?
Often regarded as the same by consumers, there lies a significant difference. Also, the complex legal frameworks, cultural stigma, and the fact that both hemp and cannabis belong to the same plant species further raise confusion.
Here, we explore the hemp vs cannabis difference in detail to understand the distinct regulations, uses, and benefits.
Sections
ToggleWhat is Hemp?

Hemp is a variety of cannabis sativa specifically cultivated to contain extremely low levels of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), typically 0.3% or less by dry weight. It is cultivated for nutritional uses rather than psychoactive effects. Hemp plants are typically taller, skinnier, and have fewer branches compared to their cannabis plants.
What is Cannabis?

Cannabis, often referred to as marijuana, includes varieties of cannabis sativa that contain higher levels of THC, typically ranging from 5% to 30% or more by dry weight. Primarily, cultivated for high THC content for its psychoactive properties and medicinal applications. Cannabis plants are bred to maximize flower production and cannabinoid concentration, producing bushier, more resinous plants with dense, aromatic buds.
Hemp vs Cannabis: Key Differences

Feature | Hemp | Cannabis |
THC Content | 0.3% or less by dry weight | 5-30% or higher THC content |
CBD Content | Varies (can be high or low) | Varies (often bred for high THC, variable CBD) |
Psychoactive? | No intoxicating effects | Yes, produces psychoactive effects |
Legal Status | Federally legal in most countries | Varies by jurisdiction, often restricted |
Common Uses | Industrial, textiles, CBD products, food | Medical, recreational, therapeutic applications |
Plant Appearance | Tall, skinny, fewer branches | Bushy, dense, more branching |
Cultivation Purpose | Fiber, seeds, CBD extraction | Flower production, cannabinoid concentration |
Common Misconceptions About Hemp and Cannabis
Among the most common cannabis vs hemp misconceptions, here are the top ones:
They’re two different plants
Not true. Hemp and cannabis are not separate species; both are varieties of cannabis sativa bred for different purposes and characteristics. The difference between cannabis and hemp is primarily legal and practical rather than botanical. Both have the same genetic foundation but have been selectively bred for distinct traits over generations.
Hemp can get you high.
Hemp has extremely low THC content (0.3% or less), making it impossible to produce intoxicating effects. Regardless of consumption method or quantity consumed, hemp lacks the THC concentration necessary to alter consciousness or produce the “high” associated with cannabis use.
CBD always comes from marijuana
CBD can be extracted from both hemp and cannabis plants. However, most commercial CBD products are derived from hemp to ensure legal compliance and avoid THC contamination.
Cannabis is illegal everywhere
The legal status of cannabis varies significantly worldwide. In the US, many jurisdictions legalized medical cannabis, recreational use, or both. Understanding cannabis vs hemp legal distinctions is essential because hemp enjoys broader legal acceptance, while cannabis laws are strict.
Relevance in Modern Society
Are cannabis and hemp the same in relevance in modern society? The answer depends on several factors:
Legal and Policy Impacts
Hemp vs cannabis legal distinctions have shaped agricultural policy, criminal justice systems, and international trade regulations. The 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp in the United States, creating a massive industry shift. The movement to legalize cannabis continues transforming legal landscapes.
Cultural and Medical Conversations
Hemp and cannabis have medical applications and cultural perceptions about them. What’s the difference between hemp and cannabis? It dictates how a product is perceived. Hemp’s mainstream acceptance makes it easy to market products compared to the stigma around cannabis-related products. However, medical cannabis research continues to reveal therapeutic potential for conditions ranging from epilepsy to chronic pain management.
Sustainability & Innovation
Hemp particularly excels as a sustainable crop, requiring minimal pesticides, improving soil health, and offering carbon sequestration benefits. Cannabis cultivation may require a more specialized approach.
Benefits of Each
Finally, it’s about the benefits each has to offer:
Hemp Benefits:

1. Legal and accessible: Hemp’s legal status in most jurisdictions makes it widely available for research, cultivation, and commercial applications. With minimal regulatory barriers, the wide accessibility has enabled rapid market development and consumer adoption.
2. Rich in CBD: Many hemp varieties are specifically cultivated for high CBD content. It makes them an ideal source for non-psychoactive therapeutic products.
3. Eco-friendly: Hemp cultivation requires minimal water, improves soil health through phytoremediation, and produces more biomass per acre than most crops.
4. Nutritional: Hemp seeds are nutritional powerhouses containing complete proteins, essential fatty acids, and important minerals.
Cannabis Benefits:
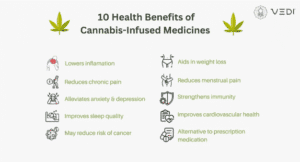
1. Medicinal relief: Cannabis’s higher THC content and diverse cannabinoid profiles offer therapeutic benefits for conditions like chronic pain, epilepsy, PTSD, and cancer treatment side effects.
2. Psychoactive effects: For recreational users, cannabis provides euphoria, relaxation, and altered consciousness. It makes it ideal for stress relief.
3. Various forms of consumption: Cannabis products can be smoked, vaporized, consumed as edibles, applied topically, or taken as tinctures. This consumption flexibility makes it possible to match individual preferences and medical needs.
4. Therapeutic potential: With deeper research revealing cannabis’s potential for treating neurological disorders, mental health conditions, and inflammatory diseases, the therapeutic benefits are expected to be wide.
Conclusion
Understanding hemp vs cannabis distinctions is essential. While both are botanically the same, they differ in THC levels, legal status, and intended uses. The choice between the two ultimately comes down to THC content, legal classification, and intended applications.




