A lot of cannabinoid discussion tends to focus on THC and CBD, but minor cannabinoids like CBC (cannabichromene) and CBG (cannabigerol) also have unique therapeutic and wellness potential. In this comprehensive guide, we conduct a deep comparison of CBC vs CBG to help consumers seeking targeted cannabinoid solutions for specific health concerns, ranging from inflammation and mood support to focus enhancement and digestive wellness.
Sections
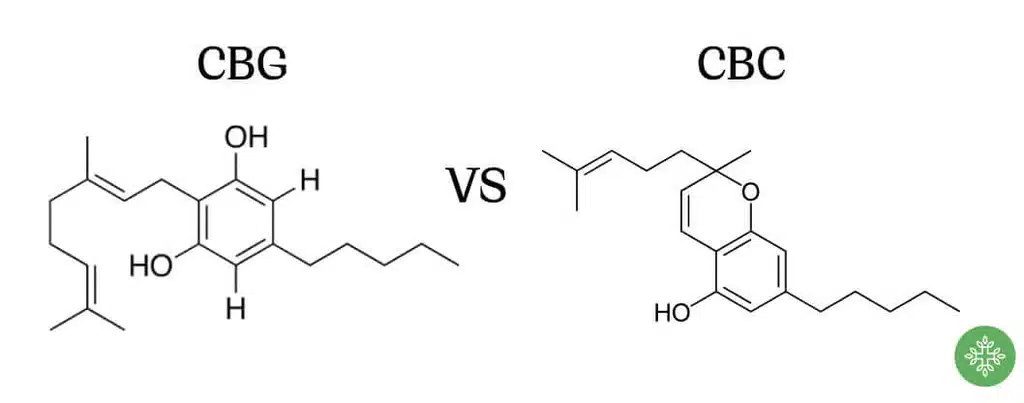
ToggleWhat are CBC and CBG?
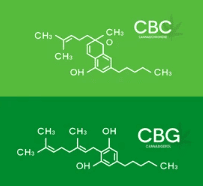
To understand the CBG vs CBC distinction, we need to understand their cannabis biochemistry and distinct therapeutic mechanisms.
What Is CBC?
CBC (cannabichromene) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that has the same chemical precursor (CBGA) as THC and CBD. However, it is produced along a distinct biosynthetic pathway in the cannabis plant. It is one of the most abundant cannabinoids in certain cannabis strains. First discovered in 1966, CBC still remains far less studied. Among the verified effects of CBC are mood elevation, reduction of inflammation, and neuroprotective properties, all without intoxication.
What Is CBG?
CBG (cannabigerol), often called the “mother cannabinoid,” is the compound that serves as the biochemical precursor from which THC, CBD, and CBC are synthesized. CBG is present in mature cannabis plants, typically in concentrations below 1%. Chemically, CBG is non-psychoactive, with promising effects for enhancing focus, anti-inflammatory activity, and supporting digestive health.
How CBC and CBG Work in the Body
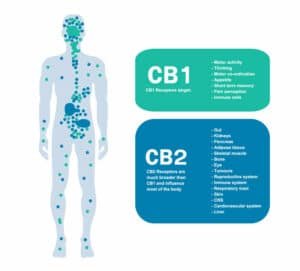
While CBC and CBG are both cannabinoids, their effect on the body varies drastically.
Interaction With the Endocannabinoid System
Both CBC and CBG interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), but through different receptor mechanisms. This is the reason they have distinct effects. These cannabinoids don’t directly bind to the CB1 receptors like THC, but they follow indirect pathways. CBC interacts with TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors, which are primarily involved in pain and inflammation perception. In contrast, CBG exhibits weak, partial agonist activity at both CB1 and CB2 receptors, while also interacting with alpha-2 adrenergic receptors.
Potency Differences
CBG and CBC don’t produce the typical “high” associated with THC. Their potential difference can be measured by comparing their therapeutic intensity and mechanisms. CBG tends to have more direct receptor interactions with moderate binding affinity. That’s why its effects can be experienced faster. On the contrary, CBC’s potency is evident through its influence on the endocannabinoid system, specifically by inhibiting the reuptake of anandamide. This makes CBC more potent for mood-related effects due to its modulation of anandamide. CBG has more profound direct anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
CBC vs CBG: What's the Difference
Feature | CBC (Cannabichromene) | CBG (Cannabigerol) |
Type of Cannabinoid | Minor cannabinoid; biosynthetic cousin to THC/CBD | “Mother cannabinoid”; precursor to THC, CBD, CBC |
Main Receptor Targets | TRPV1, TRPA1 receptors; anandamide reuptake inhibition | Weak CB1/CB2 partial agonist; alpha-2 adrenergic receptors |
Primary Effects | Mood elevation, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotection, skin health | Focus/clarity, anti-inflammatory, gut health, appetite regulation |
Potency Highlights | Strong anandamide enhancement; moderate anti-inflammatory | Direct receptor activity; potent antibacterial properties |
Best Use Cases | Mood support, skin conditions, neurological support, pain | Daytime focus, IBD/digestive issues, bacterial infections, inflammation |
Does It Cause a High? | No psychoactive effects; completely non-intoxicating | No psychoactive effects; promotes alertness without euphoria |
Common Forms | Oils, tinctures, topicals, full-spectrum products | Isolates, oils, capsules, flower (CBG-rich strains) |
Research Status | Limited but growing; promising preliminary studies | More extensive research; FDA orphan drug designation for IBD |
Legality (US) | Federally legal when hemp-derived (<0.3% THC) | Federally legal when hemp-derived (<0.3% THC) |
Effects of CBC vs CBG
Effects of CBC
- Mood elevation: CBC can affect mood by increasing anandamide availability in the brain, which inhibits its enzymatic breakdown. The increase in this “bliss molecule” is known to result in improved emotional well-being, reduced stress responses, and potential antidepressant-like effects.
- Anti-inflammatory mechanism: This cannabinoid also reduces inflammation through TRPA1 channels and other non-ECS mechanisms. The multi-target approach makes CBC a valuable anti-inflammatory compound that can provide a natural alternative for addressing inflammatory pain, arthritis, and inflammatory bowel conditions.
- Neuroprotective potential: Clinical studies suggest that CBC may support neural stem progenitor cell (NSPC) function. It can potentially promote neurogenesis and protect against neurodegenerative processes.
- Skin and topical applications: Among other uses, CBC demonstrates promising effects for acne, reducing sebaceous gland inflammation and sebum production. Also, its antibacterial properties protect against acne-causing bacteria.
Effects of CBG
- Focus & clarity: A safer alternative to sedating cannabinoids, CBG has a unique ability to promote mental alertness and cognitive clarity without stimulation. With no psychoactive effects whatsoever, it’s a safe cannabinoid for improved concentration, sustained attention, and enhanced productivity, especially for daytime use.
- Anti-inflammatory action: CBG exhibits potent anti-inflammatory effects by activating the CB2 receptor and inhibiting inflammatory cytokines. It extends its use for anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Gut health & IBD research: A segment where CBG shows the most promising application involves inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The FDA granted CBG orphan drug status for IBD treatment, which highlights its therapeutic potential.
- Appetite regulation: Like THC, this cannabinoid can also stimulate appetite. In low doses, it can increase appetite, aiding in the treatment of wasting conditions.
- Possible calming effects: CBG may simultaneously offer calming effects that reduce anxiety without sedation. It can create a balanced state of “calm alertness,” making it unique from other sedating cannabinoids.
Benefits & Use Cases: When to Choose CBC vs CBG
Best Use Cases for CBC
- Emotional balance: Individuals struggling with mood-related concerns, including depression, stress-induced emotional disturbances, or general emotional resilience enhancement, can benefit from CBC use.
- Skin wellness: For dermatological applications such as acne treatment, inflammatory skin conditions, and general skin health optimization, topical CBC products are effective as they combine antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and sebum-regulating properties.
- Neuro-support: Consider CBC for neuroprotective strategies in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases or to optimize cognitive health. This makes it particularly beneficial for aging populations.
- Complementing CBD or CBG: CBC can work synergistically with CBD or CBG, creating an entourage effect that offers full-spectrum anti-inflammatory and mood-supporting benefits.
Best Use Cases for CBG
- Daytime focus: CBG is one of the very few selective cannabinoids that offer cognitive performance enhancement during work, study, or any activity without sedation. It is excellent for day use when sustained mental clarity and concentration are mandatory.
- Gut & digestive support: CBG is excellent for inflammatory bowel conditions, digestive inflammation, or general gut health. Its targeted intestinal anti-inflammatory effects and gut barrier protective properties make it a valuable relief for these conditions.
- Inflammation-related discomfort: CBG’s direct CB2 receptor activation provides more immediate anti-inflammatory relief compared to CBC’s indirect mechanisms. This makes it more effective for chronic inflammatory conditions resistant to other treatments.
- Appetite balance: The cannabinoid has a unique appetite-modulating effect, making it helpful in addressing both decreased appetite in wasting conditions and potentially excessive appetite in metabolic disorders.
CBC vs CBG for Pain, Mood & Anxiety
Which cannabinoid leans toward which benefit?
If your primary concern is mood and anxiety, several CBC vs CBG studies suggest CBC may have an edge. Due to its anandamide-enhancing properties, it can directly influence emotional regulation systems.
CBG also has potential anxiolytic effects that can provide anxiety reduction, but not as profound as CBC.
Where the research stands: Most of the current research on CBC and CBG for pain, mood, and anxiety remains primarily preclinical. While human trials are emerging, they are still very limited. Most applications rest on preliminary science, traditional use patterns, and anecdotal reports.
Search-driven queries addressed directly: Online searchers often ask whether CBC effects outweigh CBG effects, but it is not that simple. For general anxiety and mood, CBC’s anandamide modulation is excellent; for anxiety specifically during demanding cognitive tasks, CBG’s calm-focus effects excel.
CBC vs CBG: Side Effects & Safety
Due to no psychoactive effects, both CBG and CBC demonstrate excellent safety profiles. The most commonly reported side effects from use of these minor cannabinoids include mild digestive changes, drowsiness, and alertness from CBG that might interfere with sleep. None of the cannabinoids produces psychoactive intoxication, addiction potential, or severe adverse reactions.
However, as with other cannabis products, before using these cannabinoids, consult healthcare providers about potential interactions. Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should avoid cannabinoid supplementation.
How They Compare to Other Cannabinoids
CBD → Most widely studied non-psychoactive cannabinoid, CBD is known for its broad-spectrum therapeutic effects. It has anti-anxiety properties that can help in seizure reduction. Its general anti-inflammatory activity, achieved through multiple mechanisms, shows promise for several conditions.
CBC → It is distinguished due to its unique anandamide modulation. Neither CBD nor CBG provides such modulation. It means CBC has potentially superior mood-elevating effects while maintaining similar anti-inflammatory properties.
CBG → Its focus-enhancing properties differ from both CBD and CBC. Combined with specific gut health benefits and antibacterial effects, it complements CBD’s calming properties and inflammation benefits.
Legal Status & Availability
CBC Legality
CBC derived from hemp containing less than 0.3% delta-9 THC is federally legal. Most state laws generally mirror federal hemp legality, making CBC legal, though some jurisdictions maintain restrictions.
CBG Legality
Like CBC, hemp-derived CBG remains federally legal under the Farm Bill, with the same THC content restrictions applying.
Can You Use CBC and CBG Together?
Yes. Combining CBC and CBG is often a way to enhance therapeutic outcomes through the entourage effect. These cannabinoids work synergistically to amplify each other’s benefits. A combination of these cannabinoids can address multiple therapeutic targets simultaneously. It can be highly beneficial for individuals with inflammatory conditions that require both acute relief and sustained improvement, as well as mood support and stress management.
CBC vs CBG: Which One Should You Choose?
- For mood support → Choose CBC for its anandamide-enhancing properties. It can naturally elevate emotional well-being.
- For focus & clarity → CBG is a definite choice due to its unique alertness-promoting effects without stimulation. It offers cognitive performance enhancement during demanding mental tasks without any “high”.
- For inflammation → CBC and CBG both offer anti-inflammatory benefits. For inflammation, combine both for synergistic anti-inflammatory effects.
- For skin wellness → CBC is a better choice for dermatological applications, particularly acne, due to its specific sebum-regulating and antibacterial properties.
- For digestive or gut support, CBG is excellent for relieving inflammatory bowel disease and has specific mechanisms that protect gut barrier integrity and reduce intestinal inflammation.
- For general wellness → Consider full-spectrum products containing both CBC and CBG alongside CBD for general wellness.
Conclusion
While the differences between CBC and CBG exist at the molecular level, their therapeutic benefits are complementary. CBC affects mood elevation, skin health, and neuroprotection through anandamide modulation, while CBG offers focus enhancement, gut health support, and potent anti-inflammatory activity. Whether you choose CBC or CBG depends on your health goals and preferences.