Closed loop extraction refers to isolating substances using a solvent in a sealed system, thus preventing solvent exposure. There are 2 main types of closed-loop extraction systems- passive and active. If you need to choose the best system, it depends on various factors like cost, operational complexity, and efficiency. Below, we discuss the main differences between active and passive closed-loop extraction.
Sections
ToggleHow Passive Solvent Recovery Works
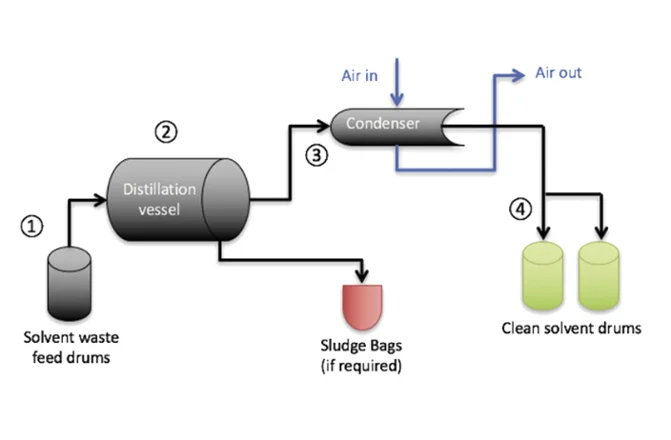
A passive recovery system uses heating and cooling temperatures to adjust the pressure and recover ethanol or hydrocarbon solvent. This way, the solvent is recovered through distillation and cooling or dry ice systems. This solvent recovery method relies on temperature manipulation to modulate the pressure and thus recover solvent.
Further, this method works on the principle of gases moving towards lower-pressure areas. So, by heating the gas in the collection tank and cooling the solvent recovery tank, this system moves the gas from one location to the other. As the vapor cools below its boiling point, it re-condenses into liquid form, thus making it ready for reuse.
Passive vs. Active Closed Loop Extraction
Choosing between passive and active closed-loop extraction depends on the operator’s preference. As active recovery has been the go-to method for solvent recovery, most operators are familiar with it and have more choice for it based on comfort and the fact that active recovery is a bit faster than passive.
Many operators have not tried the passive method as the extraction they may have bought does not support recovery in an efficient way. But with the latest developments in technology and the correct pairing of chilling and heating equipment, passive extraction can be an efficient, safe and cost-effective solution for closed-loop extractors.
Passive vs Active Closed Loop Extraction: Key Differences
Feature | Passive Recovery | Active Recovery |
Recovery | Lower recovery speed | Rapid speed |
Cost | Reduced cost | Slightly more costly |
Maintenance | Lower maintenance needs | Needs more maintenance |
Equipment Required | Simple setup | Requires advanced setup |
Ideal use | Industries like woodworking, textiles and small scale manufacturing use passive method | Industries like pharmaceutical, petrochemicals and large scale chemical processing rely on active method |
Control over process | Simple control | Precise control |
Pros and Cons of Passive Recovery
Pros
1. Lower setup cost
Passive recovery is cheaper as the recovery pumps add between $20000 and $50000 in the startup cost depending on the extraction operation size.
2. Fewer components
One of the pros of passive recovery is that it needs less equipment and doesn’t require any additional components like a gas compressor.
3. Minimal maintenance
Passive extraction is a simple process that does not require additional steps or components outside the extractor. This makes the process simple and easy to operate.
4. Safety
Companies like the ease of implementation offered by passive recovery as it integrates seamlessly into existing environments. It also promotes sustainability by reducing the carbon footprint compared to other energy-intensive methods.
Cons
1. Slower recovery
Despite the benefits, it also has some limitations, such as the process taking longer to reach the desired recovery level. This can create delays.
2. Performance varies
The effectiveness is mainly dependent on ambient conditions like temperature changes that can impact the natural process’s efficiency.
3. Limited scalability
Passive recovery may not suit all types of solvents, mainly those that require specific evaporation or condensation conditions. It is thus essential to closely evaluate such concerns before adopting the method in your company operations.
Pros and Cons of Active Recovery
Pros
1. Faster solvent recovery
One of the key benefits is that the active recovery method delivers a quick recovery rate for operations that demand fast solvent turnover.
2. High throughput
Active recovery offers consistent operations with repeatable results and is also far more efficient. Its ability to repeat the processes makes it easier actually to forecast everything- be it product or cost.
3. Consistent performance
Active solvent recovery offers consistent operation with repeatable results and is a far more efficient approach to recovering hydrocarbons. The ability to repeat procedures makes forecasting everything from time to products and costs easier.
4. Process control
This method offers control, thus allowing the companies to ensure consistent solvent purity and quality.
Cons
1. Higher cost
The active method is an efficient form of recovery that is easily scalable. But as the operations scale in size, the recovery pump price also increases.
2. Increased complexity
Adding any new equipment to the method also means that there will be more maintenance and the recovery pumps will need repairs when they are more operated.
3. Maintenance required
Special equipment also needs maintenance and capital investment. Active recovery may introduce complex procedures into the operations, requiring skilled people to manage the system.
4. Safety protocols
Regular safety and maintenance like inspections of the seals and gaskets are required to prevent leakage and ensure operational safety.
Which Recovery System Should You Choose?
You should choose passive recovery if:
- You are a beginner as there is no need for electrical equipment to move the solvent. These systems are efficient with recovery speeds
- They are favorable if large-scale production is not required
- If you have much time to process and/or access bulk dry ice.
On the other hand, you should choose active recovery if:
- The speed and production amount are a requirement, or dry ice is tough to come by; you can choose the active system.
- You need faster recovery time.
- If you require heavy production volume or if you are the one who uses large systems.
Conclusion
Choosing between passive or active closed-loop extraction depends largely on one’s specific requirements, budget, and expertise. If you prefer low upfront costs and a simple method, a passive system may be just right for you. However, the active system may be a better choice for those who want higher efficiency and wish to manage complex systems. Both systems have their merits and can extract substances effectively when appropriately used, but you must understand their operation differences and limitations when making a decision.




