Butane Hash Oil extraction is a widely known process in the cannabis industry, but it is also one of the most hazardous when safety standards are not strictly followed. BHO extraction involves the use of pressurized and highly flammable gases, which makes the process especially dangerous in poorly controlled environments. Fires, explosions, chemical exposure, and contamination incidents are most often linked to improper BHO extraction methods and lack of professional oversight.
Understanding the dangers of BHO extraction and the safety measures used in professional facilities is essential for reducing risk and protecting both operators and consumers.
Sections
ToggleThe Dangers of BHO Extraction

The dangers associated with BHO extraction mainly arise from flammable solvents, confined spaces, pressurized equipment, and inadequate environmental controls. These risks increase significantly when extraction is performed using improvised setups or without proper training.
1. Flammable Solvents
Butane is the most commonly used solvent in BHO extraction, and it is extremely flammable. Even a small leak can lead to ignition if exposed to static electricity, electrical switches, or non-rated equipment. Because butane is heavier than air, it can accumulate in low areas and enclosed spaces, creating a high explosion risk.
Other types of gas for BHO extractions share similar safety concerns. While pressure levels and volatility may vary, all hydrocarbon gases used in BHO extraction require strict containment and monitoring to prevent fires and explosions.
2. Poor Ventilation
Poor ventilation is one of the leading causes of BHO extraction accidents. Without adequate airflow, leaked gas can build up rapidly and form an explosive atmosphere. In addition to fire hazards, poor ventilation can lead to oxygen displacement, increasing the risk of dizziness, impaired judgment, and asphyxiation.
Professional BHO extraction environments are designed with ventilation systems that actively remove flammable gases and maintain safe air conditions throughout the extraction process.
3. Equipment and Pressure Failures
BHO extraction systems operate under pressure, which makes equipment integrity critical. Failures often occur due to worn seals, damaged valves, loose fittings, or the use of non-rated components. Even small leaks in BHO extraction tools can result in dangerous gas accumulation.
Pressure-related incidents are more common when extraction is attempted using homemade or modified equipment rather than certified systems designed specifically for BHO extraction.
4. Chemical Exposure
Chemical exposure is another major safety concern in BHO extraction. Direct inhalation of butane can cause headaches, nausea, respiratory irritation, and loss of coordination. In enclosed spaces, exposure becomes more severe due to oxygen displacement.
Skin and eye contact with solvents or contaminated surfaces can also cause irritation or injury. These risks highlight why controlled handling environments and protective measures are essential during BHO extraction.
5. Thermal Burns
Thermal burns can occur during BHO extraction due to contact with heated surfaces, pressurized components, or temperature-controlled equipment. Burns may also happen during equipment maintenance or cleaning if systems have not cooled properly.
Although heating steps are often associated with later stages, extraction environments still present burn hazards that must be managed through proper equipment design and handling procedures.
6. Residual Solvents and Contamination Risks
Improper BHO extraction can result in residual solvents and contamination in the final product. Contamination may come from solvent residues, degraded equipment components, or poor sanitation practices. These issues directly affect the safety of different types of BHO, as texture, consistency, and purity are closely linked to extraction quality.
Residual solvents are especially concerning when considering BHO consumption methods, since inhalation and ingestion increase the importance of solvent removal and purity standards.
7. Environmental Impact
BHO extraction also carries environmental risks when gases are released into the atmosphere or waste is improperly handled. Hydrocarbon emissions contribute to volatile organic compound release, while poor disposal practices can lead to environmental contamination.
Professional BHO extraction facilities address environmental concerns through containment, solvent recovery, and compliant waste management practices.
Safety Measures for BHO Extraction
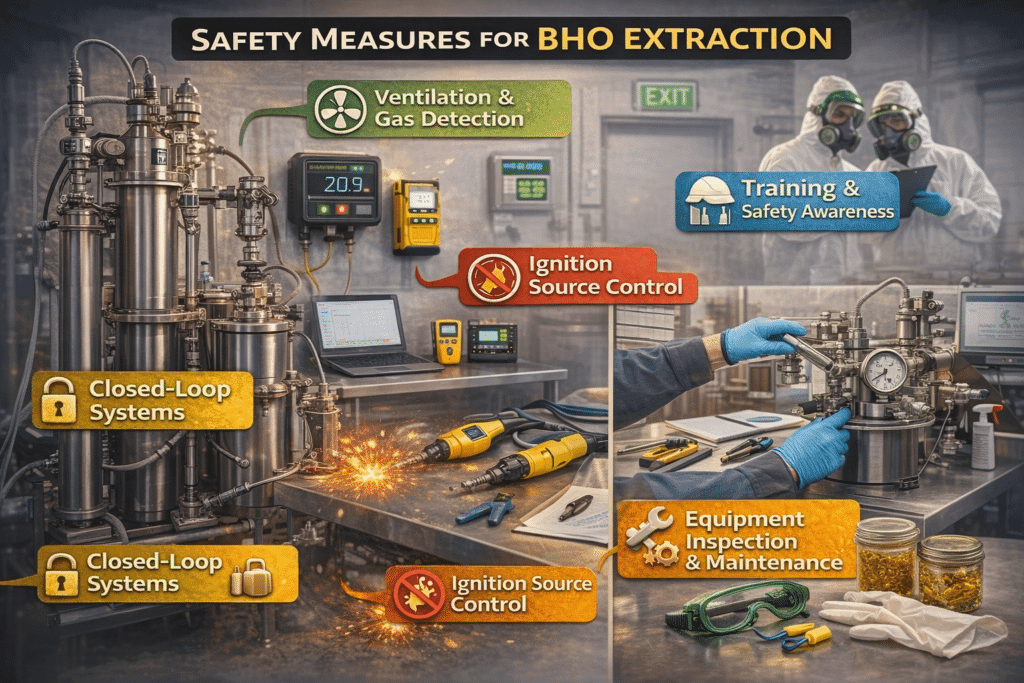
Reducing risk in BHO extraction depends on engineered safety controls, trained operators, and regulated facilities. Safe operations focus on containment, ventilation, equipment monitoring, and strict control of ignition sources.
1. Closed-Loop Systems
Modern BHO extraction relies on closed-loop systems that contain solvents within sealed equipment. These systems reduce the likelihood of gas release and significantly lower the risk of fire or explosion. Closed-loop BHO extraction methods are designed to support safer solvent recovery and controlled processing conditions.
2. Ventilation and Gas Detection
Safe BHO extraction environments use engineered ventilation systems and gas detection equipment to prevent solvent buildup. Continuous monitoring allows early detection of leaks and helps maintain safer air quality throughout the extraction process.
3. Ignition Source Control
Controlling ignition sources is a critical part of BHO extraction safety. Electrical equipment must be rated for hazardous environments, and open flames, sparks, and static discharge must be eliminated from extraction areas. Even minimal ignition sources can trigger serious incidents if flammable gas is present.
4. Equipment Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of BHO extraction tools help identify leaks, pressure issues, and component wear before they become dangerous. Professional operations follow documented maintenance schedules and replace parts according to manufacturer specifications to maintain safe operating conditions.
5. Training and Safety Awareness
Many BHO extraction incidents occur due to human error rather than equipment failure. Proper training improves hazard awareness, handling decisions, and emergency response. Trained operators understand the risks associated with different BHO extraction methods and follow established safety procedures consistently.
6. Consumer Safety and Product Quality
Extraction safety directly impacts consumer health. Residual solvents and contamination risks emphasize why proper BHO extraction is essential for producing safer concentrates. Consumers using various BHO consumption methods rely on clean extraction processes to reduce inhalation and ingestion risks.
Conclusion
BHO extraction presents serious safety challenges related to flammable solvents, poor ventilation, pressure systems, and contamination risks. Safe operations depend on closed-loop containment, engineered ventilation, certified equipment, and trained professionals. For these reasons, BHO extraction should only be performed in controlled, compliant environments that prioritize safety at every stage of the process.
FAQs
Yes, BHO extraction can be dangerous because it uses pressurized, highly flammable gases, which increases the risk of fire, explosion, and chemical exposure if proper safety controls are not in place.
Explosions usually happen when butane leaks and accumulates in a poorly ventilated area, then ignites from an ignition source such as static electricity, a spark, or non-rated electrical equipment.
No. Residential or indoor environments typically lack the ventilation, monitoring, and hazard-rated systems needed to manage flammable gases safely.
Yes, If extraction and quality controls are poorly managed, BHO may contain residual solvents, which can pose health risks, especially for inhalation-focused BHO consumption methods.
Ventilation helps prevent flammable gas buildup and reduces oxygen displacement risks, which lowers the chance of fire, explosion, and inhalation hazards.
Leaks, seal failures, or pressure-related equipment failures can release flammable gas and create dangerous conditions quickly, which is why certified, pressure-rated systems and maintenance are critical.




