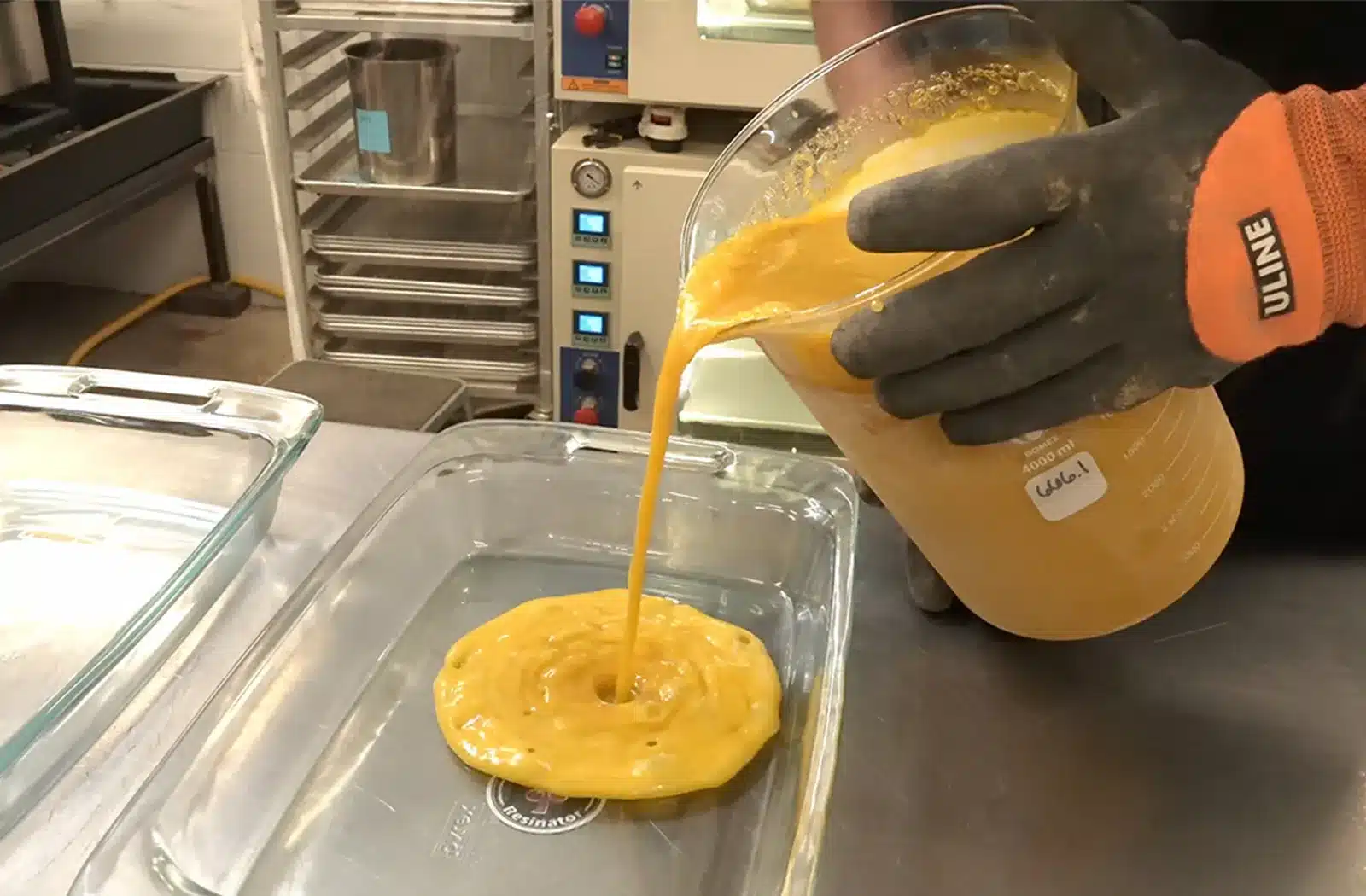
Light hydrocarbon extraction is becoming popular in the cannabis industry for producing high-quality cannabis concentrates. Manufacturers are interested in this extraction process because of its superior efficiency and versatility compared to other extraction methods.
Here we explore how this sophisticated process can efficiently extract cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis biomass, creating everything from shatter and wax to live resin and high-terpene full-spectrum extracts.
Sections
ToggleWhat Is Light Hydrocarbon Extraction?
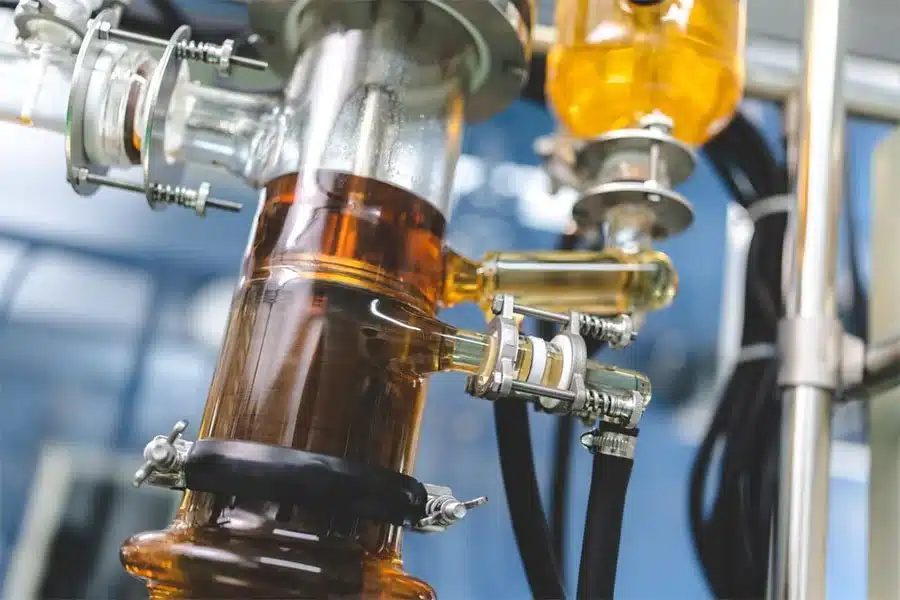

Light hydrocarbon extraction is a solvent-based extraction method that uses liquefied light petroleum gases, primarily butane and propane, to separate cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis plant material. The extraction occurs within a closed-loop system to improve efficiency by maintaining the solvents in their liquid state through controlled temperature and pressure conditions. The term “light” is associated with the process because the hydrocarbons have relatively low molecular weights and boiling points.
What Are Hydrocarbons in Extraction?
Hydrocarbons are compounds made from hydrogen and carbon atoms that act as effective solvents for dissolving cannabis compounds. Due to their non-polar structure, they can dissolve and separate cannabinoids and terpenes while leaving behind unwanted water-soluble compounds.
In light hydrocarbon extraction, two widely used solvents are:
- Butane: A four-carbon hydrocarbon (C4H10), it has a low boiling point of 31.1°F (-0.5°C). It is an excellent solvent for producing harder, more potent extracts.
- Propane: A three-carbon hydrocarbon (C3H8) with a lower boiling point of -43.6°F (-42°C), it is most suitable for preserving terpenes along with cannabinoids and creating softer, more aromatic extracts.
Light Hydrocarbon Extraction Process
The extraction process is similar to other extraction processes involving these steps:
- Loading Biomass
First, cannabis plant material is prepared for extraction through grinding. Then it is loaded into extraction columns within the closed-loop system. Preparation of biomass is essential to ensure optimal solvent contact and efficient extraction of desired compounds.
- Solvent Introduction
Chilled liquid hydrocarbon solvent is introduced into the closed-loop system through the material column under controlled pressure and temperature conditions. Temperature is typically maintained around -40°F (-40°C) to preserve temperature-sensitive terpenes.
- Extraction and Separation
The liquid solvent dissolves cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant material through molecular interaction. The solution then passes through collection vessels to separate dissolved compounds from the spent plant material.
- Recovery of Hydrocarbons
The solvent is recovered from the cannabinoid solution through controlled evaporation processes. Recovery systems utilize vacuum pumps and temperature control to separate the hydrocarbon solvent from the concentrated oil.
- Purging and Post-Processing
The final extract undergoes vacuum purging to remove residual solvents. Post-processing takes place depending on the product and potency or cannabinoid profile required. It can include dewaxing, filtration, and specific purification techniques.
Safety Considerations in Light Hydrocarbon Extraction

Like with any extraction process, safety must be prioritized:
Flammability and explosion risks:
Hydrocarbons are highly flammable gases requiring strict safety protocols to prevent ignition sources and potential explosions.
Best practices for lab setup:
Light hydrocarbon extraction facilities must meet C1D1 (Class 1, Division 1) safety standards, which mandate explosion-proof equipment, gas monitoring systems, and proper ventilation to contain volatile solvents safely. Also, closed-loop systems are safest as they prevent solvent leaks and exposure to heat sources.
Importance of professional handling:
Staff must be trained to operate extraction equipment due to the complex safety requirements and potential hazards.
Equipment for Light Hydrocarbon Extraction
Specialized equipment is required for light hydrocarbon extraction:
1. Closed-Loop Extraction Systems: These sealed systems are designed for efficiency, recycling, and safety. They prevent solvent loss and contamination while maintaining safe operating conditions through integrated pressure vessels, recovery pumps, and automated controls.
2. Solvent Recovery Units: Specialized systems that separate and recycle hydrocarbon solvents from extracted oil, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
3. Filtration and Post-Processing Tools: Equipment like vacuum ovens, dewaxing columns, and color remediation systems for refining crude extracts into high-quality extracts.
Advantages of Light Hydrocarbon Extraction
There are several advantages of this method:
1. High-quality extracts with terpene preservation: The Low boiling point of light hydrocarbons makes it possible to maintain delicate terpene profiles and produce full-spectrum concentrates.
2. Efficient and cost-effective: Closed loop extraction systems produce fast processing times, high yields, and solvent reusability.
3. Versatile product outputs: A Single light hydrocarbon extraction cycle can produce multiple product types, including shatter, wax, live resin, and sauce.
Limitations and Challenges
Before considering this extraction method, consider these limitations:
- Safety risks: Light hydrocarbons are flammable, requiring extensive safety measures, specialized facilities, and trained personnel to operate safely.
- Regulatory restrictions: Regulations associated with hydrocarbons are strict, with some jurisdictions prohibiting these methods entirely.
- Initial investment costs: Setting up a compliant light hydrocarbon extraction facility will require significant capital investment in specialized equipment and safety systems.
Conclusion
Light hydrocarbon extraction is an excellent method offering unmatched efficiency, product quality, and versatility in the extraction industry. It helps save costs while producing more versatile products. However, these benefits come with inherent safety challenges and regulatory complexities. Considering this extraction method, you need to account for proper staff training, compliance with safety regulations, and investment in quality equipment.