The BHO extraction process is a hydrocarbon-based method used to separate cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis plant material using butane as a solvent. This process is widely adopted in regulated markets due to its efficiency, scalability, and ability to preserve aromatic compounds. When performed using professional systems, BHO extraction produces highly concentrated extracts that are later refined for consistency, purity, and consumer safety. Understanding the BHO extraction process helps explain why it remains one of the most common techniques in modern cannabis concentrate production.
Sections
ToggleWhat Is BHO Extraction?

BHO extraction, short for Butane Hash Oil extraction, relies on butane’s ability to dissolve cannabinoids such as THC and CBD along with naturally occurring terpenes. Because butane operates at low temperatures, it minimizes damage to heat-sensitive compounds. This makes Bho extraction especially valuable for producing flavor-rich concentrates intended for various end-use applications.
BHO Extraction Process: How It Works
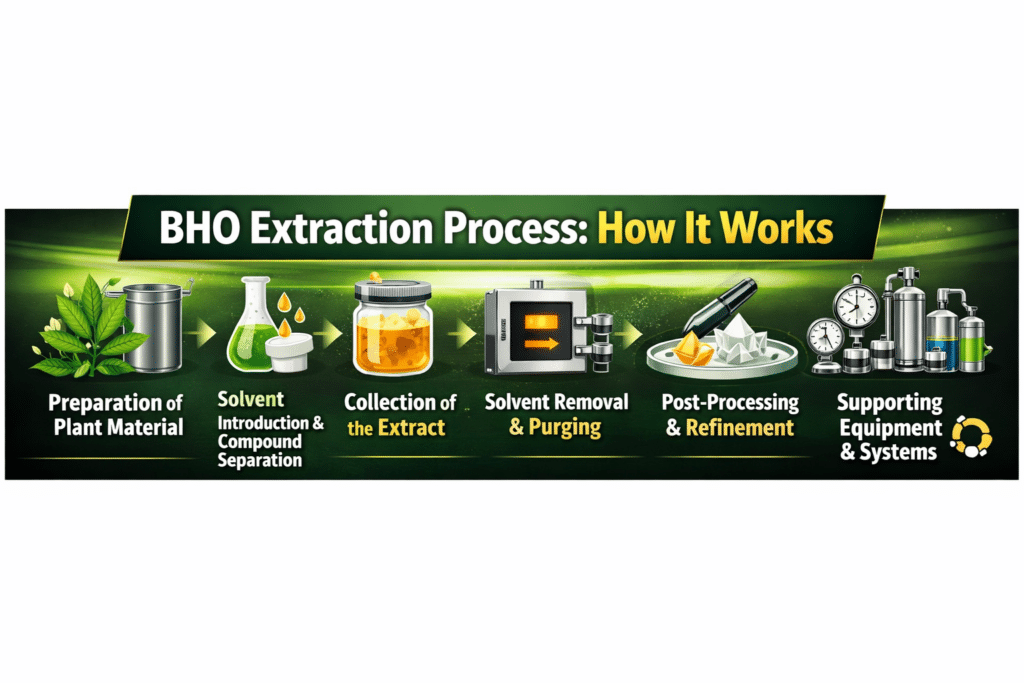
The BHO extraction process typically follows six core stages from preparation to refinement in professional production environments.
1. Preparation of Plant Material
The BHO extraction process begins with prepared cannabis plant material being placed into an extraction vessel, commonly a sealed stainless steel column. Proper preparation supports efficient solvent interaction while helping preserve cannabinoid and terpene content. This stage sets the foundation for consistent results throughout the Bho extraction workflow.
2. Solvent Introduction and Compound Separation
During this stage, a hydrocarbon solvent is introduced to interact with the plant material. Among the types of gas for BHO extractions, n-butane is most commonly referenced due to its ability to dissolve cannabinoids and terpenes effectively. As the solvent passes through the material, desirable compounds are separated from the plant matter.
3. Collection of the BHO Extract
The solvent carrying dissolved cannabinoids and terpenes moves into a separate collection chamber. At this point in the BHO extraction process, the extract exists as a mixture of oil and solvent. Further refinement is required before the extract can be considered stable or usable.
4. Solvent Removal and Purging
Solvent removal is a critical phase of the BHO extraction process. Controlled conditions are used to eliminate residual butane from the extract. Effective purging directly impacts aroma, stability, and compliance, which is why safety concerns in BHO extraction are closely associated with this stage. Issues at this point are also commonly addressed when troubleshooting BHO extraction outcomes.
5. Post-Processing and Refinement
Once solvent removal is complete, extracts may undergo additional refinement to achieve desired physical characteristics. Adjustments during post-processing influence texture and stability, which explains how the same BHO extraction process can result in multiple concentrate forms. These refinements are what lead to the different types of BHO seen in the market today. In some cases, producers apply advanced BHO extraction techniques to further improve consistency or terpene preservation.
6. Supporting Equipment and Systems
Throughout all stages, professional facilities rely on specialized BHO extraction tools designed to manage pressure, temperature, and solvent recovery. Closed-loop systems are widely used to improve efficiency and reduce operational risk, supporting consistent outcomes across batches.
Safety Considerations in BHO Extraction
Due to the flammable nature of hydrocarbons, safety concerns in BHO extraction remain a central topic across the industry. Professional facilities follow strict operational standards related to ventilation, pressure control, and equipment certification. These safeguards are essential not only for worker safety but also for ensuring clean, compliant final products.
From Extraction to End Use
After refinement, BHO concentrates are incorporated into a wide range of products and formats. These extracts support multiple BHO consumption methods, including vaporization, dabbing, and infused formulations. The flexibility of BHO extracts is one of the main reasons the extraction process continues to be widely used in commercial settings.
Why the BHO Extraction Process Remains Relevant
Despite the emergence of alternative extraction methods, the BHO extraction process remains a cornerstone of concentrate manufacturing. Its balance of efficiency, potency, and terpene preservation keeps it relevant for producers focused on consistent, high-quality outputs.
The BHO extraction process remains one of the most widely used methods for producing cannabis concentrates due to its efficiency, scalability, and ability to preserve cannabinoids and terpenes. From solvent interaction and purging to post-processing and safety controls, each stage plays a role in determining extract quality and consistency. Understanding how the BHO extraction process works provides valuable context for evaluating concentrate production methods while supporting informed discussions around safety, equipment, and end-use applications.
FAQs
The three most commonly discussed cannabis extraction methods are hydrocarbon extraction, CO₂ extraction, and solventless extraction. Hydrocarbon extraction includes BHO extraction and uses solvents like butane to dissolve cannabinoids and terpenes. CO₂ extraction relies on pressurized carbon dioxide and is often used for oils and tinctures. Solventless extraction methods such as rosin use heat and pressure without chemical solvents.
The yield of BHO extraction varies depending on factors such as plant material quality, cannabinoid content, and processing efficiency. In commercial settings, yields are often considered relatively high compared to many other extraction methods, which is one reason the BHO extraction process is widely used. Final output is typically measured as a percentage of extract obtained from the original plant material.
The primary BHO solvent is butane, a hydrocarbon that effectively dissolves cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis plant material. In professional systems, refined forms of butane or controlled hydrocarbon blends are used to improve efficiency and consistency. Proper solvent removal is a critical part of the BHO extraction process to ensure product safety and compliance.
BHO extract refers to concentrates produced specifically through butane-based extraction, while the term “wax” describes a texture or consistency rather than an extraction method. Wax can be a type of BHO extract, but not all wax-like concentrates are produced using butane. The difference lies in how the extract is made, not just how it looks.




